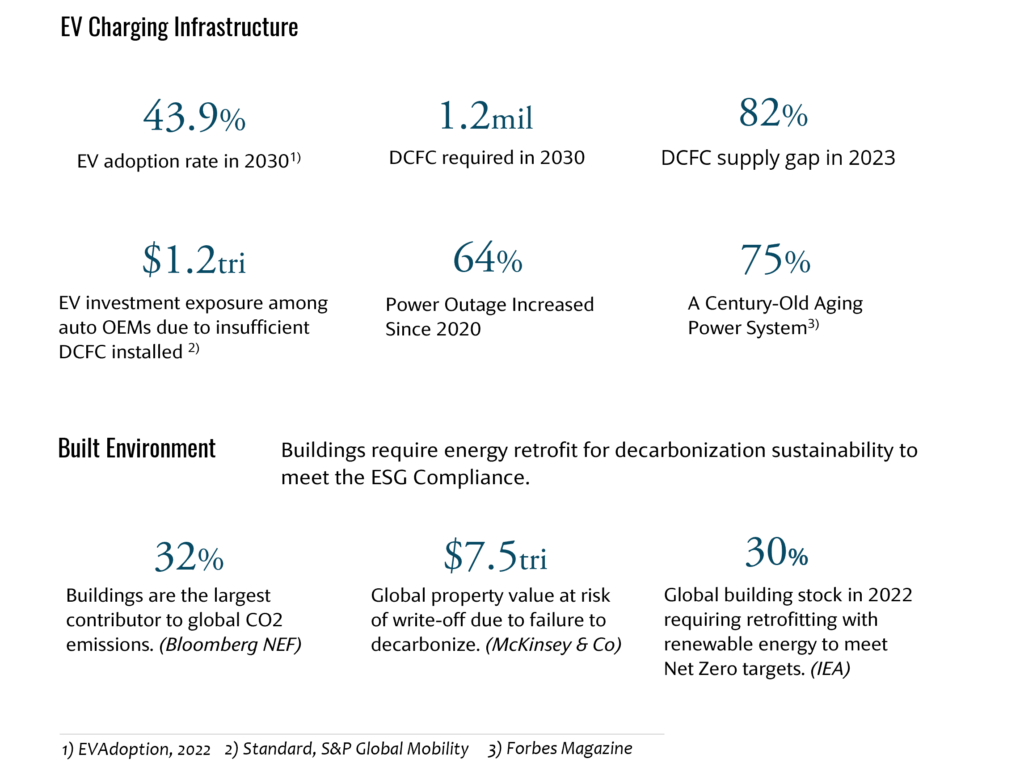Business Insight
1. Pain Points of EV Charging Market



Insufficient Charger Supply
- Low DCFC deployment rate at 18% (NREL)
- The lack of sufficient charging stations contributes to EV owners’ “Range Anxiety”, causing delays in wider EV adoption.
- Most DC charging stations are equipped with only 3 to 5 chargers, leading tofrequent long wait times for users.
- The infrastructure cost for DC fast chargers is 50% to 300% higher than that of traditional gas pumps, making it difficult to scale and develop more charging stations.
Immature Technology
- 25% of DCFCs installed by CPOs are out of service. Many stations face technical issues, leading to operational downtime.
- Failures arises in problems with power module, network communication, and software, affecting overall reliability
- Supply chain issues: The lack of major U.S. DC fast charger (DCFC) manufacturers has led to reliance on imported chargers, resulting in quality control inconsistencies.
Aged & Congested Grid
- $170 Billion Annual Business Loss: This critical issue results in significant financial losses for the industry each year.
- Most CPOs depend on outdated legacy grids, which can exacerbate grid congestion.
- Grid congestion worsens with the increasing adoption of EVs and AI technologies.
2. Net Zero Dynamics : New Paradigm & New Opportunity

The global shift towards a low-carbon economy is accelerating, with climate change acknowledged as one of the most pressing challenges of our time. The Paris Agreement, uniting 192 nations in a historic commitment to achieve Net Zero emissions by 2050, underscores the urgency of collective action. Meeting this target will demand an estimated $194 trillion in investments by 2050 (Bloomberg NEF, McKinsey & Co.).
Electrification and decarbonization technologies are pivotal in this effort, particularly as transportation and buildings contribute significantly to global CO2 emissions, accounting for 35% and 32%, respectively.
ESG regulations increasingly mandate businesses and property owners to decarbonize their operations and real estate portfolios. Climate technologies—such as electric vehicles (EVs), battery energy storage systems (BESS), solar power, EV chargers, microgrids, and distributed energy resources (DERs)—are now critical to achieving compliance, while enhancing asset value and sustainability.
3. Climate Abnormality and Climate Technology Investment Requirement

4. Key Figures Addressing Trend and Direction of Climate Transition